Exploring the Caribbean National Forest: A Comprehensive Overview


Intro
The Caribbean National Forest represents a unique ecological treasure. Nestled in the Caribbean region, this forest is not just a natural wonder; it is also a vital area for biodiversity and environmental study. The need for preserving such areas has never been more pressing. This forest showcases the intricate interrelationships between various species and their habitats. Understanding these dynamics is key to successful conservation efforts.
As we turn to the subsequent sections, we will delve into the ecology of the forest, highlighting its biodiversity and exploring sustainable practices that can be adopted. Furthermore, there is an essential role for local communities in stewardship that we must recognize. The interplay of these elements will be examined in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Caribbean National Forest.
Forest Ecology and Biodiversity
Importance of Forest Ecosystems
Forests are essential to the health of our planet. They provide numerous services including carbon sequestration, oxygen production, and habitat for a multitude of species. In the Caribbean National Forest, these elements are especially critical. The dense vegetation acts as a natural filter for air pollutants and contributes to climate regulation. The forest also plays a crucial role in maintaining water quality and regulating the water cycle.
Flora and Fauna in Woodlands
The biodiversity within the Caribbean National Forest is remarkable. It is home to various species of plants and animals, many of which are endemic. The flora ranges from towering trees to vibrant understory plants. Notably, species such as the Coqui de la Isla and the Lynda Amphitrite can be found here, illustrating the unique ecological attributes of the area.
The fauna includes a variety of birds, reptiles, and insects that are adapted to the forest's specific climates. This biodiversity is not only vital for the ecosystem's health but also contributes significantly to its resilience against environmental changes.
"Diverse ecosystems like the Caribbean National Forest are critical for the long-term sustainability of our natural world."
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Techniques for Responsible Management
To ensure the preservation of the forest's ecology, sustainable forestry practices must be prioritized. Responsible management includes practices such as selective logging, which minimizes impact while still allowing for economic benefits to be realized. Techniques like agroforestry also promote biodiversity while enhancing local agriculture.
Certification Schemes and Standards
Certification schemes like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) offer guidelines and standards for sustainable practices. By adhering to these guidelines, forestry operations can be monitored for compliance, ensuring that forest resources are managed responsibly and sustainably.
Community Engagement and Stewardship
Role of Local Communities
Local communities play an integral role in the conservation efforts surrounding the Caribbean National Forest. Their traditional knowledge of the ecosystem can provide insights that enhance conservation strategies. Engaging communities in management practices helps create a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the forest.
Volunteer Opportunities for Engagement
There are numerous ways individuals can get involved in preserving this critical ecosystem. Volunteer opportunities exist, allowing people to contribute to tree planting, wildlife monitoring, and habitat restoration. Engaging with local organizations also amplifies the impact of individual efforts, promoting a more substantial community-wide approach to conservation.
By exploring these elements, it becomes evident that the Caribbean National Forest is not just a forest—it's a vital part of our global ecosystem, calling for informed engagement and dedicated stewardship.
Intro to the Caribbean National Forest
The Caribbean National Forest, also known as El Yunque National Forest, represents a unique and vital environment in the heart of Puerto Rico. Its importance transcends mere scenic beauty or recreational opportunities; it serves as a critical habitat for a diverse range of species and plays a significant role in global ecological health. By understanding the intricacies of this forest, we can better appreciate its contributions to biodiversity and conservation.
This introduction aims to illuminate the various facets of the Caribbean National Forest, highlighting its geographical significance and historical context. These elements form a foundation for subsequent discussions about the diverse flora and fauna found within, as well as the ecological services it provides.
Geographical Overview
The Caribbean National Forest is perched in the northeastern part of Puerto Rico. Spanning approximately 28,000 acres, it is characterized by lush greenery, steep terrain, and a tropical climate. The elevation ranges from about 1,000 to nearly 3,500 feet above sea level. This variance creates a multitude of microclimates, fostering a wide variety of plant and animal habitats.
The forest is located in close proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, which influences its weather patterns. Frequent rainfall, often exceeding 200 inches annually, ensures that the terrain remains fertile and vibrant throughout the year. The forest contains various ecosystems, including subtropical rainforests, montane forests, and even cloud forests at higher elevations. This diversity contributes to its status as a biologically rich region, making it an important area for ecological study.

Historical Background
The history of the Caribbean National Forest is as rich as its biodiversity. Originally, the landscape was inhabited by the Taíno people, who utilized the forest's resources sustainably. With the arrival of European colonizers in the 15th century, significant alterations began to take place. Deforestation became rampant as agricultural practices expanded, disrupting the delicate ecosystems found in the area.
In the early 20th century, the United States government recognized the ecological and recreational value of the land. In 1903, it was designated as the Luquillo Forest Reserve. The forest eventually gained national recognition in 2003, becoming part of the National Forest System. These changes reflect an evolving understanding of the importance of preserving natural resources not just for their direct utility but also for their intrinsic ecological value.
"Understanding the past of the Caribbean National Forest allows us to appreciate its complexity and the necessity for ongoing conservation efforts."
The various historical phases have influenced the forest's present conditions, shaping the ecological landscape that serves countless species and enhancing our understanding of environmental stewardship. As we progress into subsequent sections, the focus will shift to the biodiversity contained within, underscoring the significance of this forest as an invaluable ecological asset.
Biodiversity within the Forest
Biodiversity is a cornerstone of the Caribbean National Forest's ecological integrity. This region's varied ecosystems house a complex network of life, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. The interdependence of species, whether they are plants, animals, or microorganisms, contributes to resilience against environmental changes. It is important to understand that biodiversity is not just a collection of species; it defines the health and functionality of the entire ecosystem.
Flora of the Caribbean National Forest
The flora of the Caribbean National Forest is remarkably diverse, encompassing a wide range of plant species. Tropical hardwood trees, such as Tabebuia heterophylla and Swietenia macrophylla, dominate the landscape, shaping the forest’s unique characteristics. These trees provide essential habitat and resources for numerous species. Moreover, undergrowth vegetation flourishes in the shade, showcasing ferns, shrubs, and various herbs that form the lower strata of the forest.
Bamboo species also appear in certain areas, contributing to the forest’s unique scenery and helping stabilize the soil. Medicinal plants, which have been used by local communities for generations, add cultural and practical value to this biodiversity. The intricate layers of vegetation ensure that the ecosystem functions effectively, offering critical habitat for wildlife and helping to regulate the local climate.
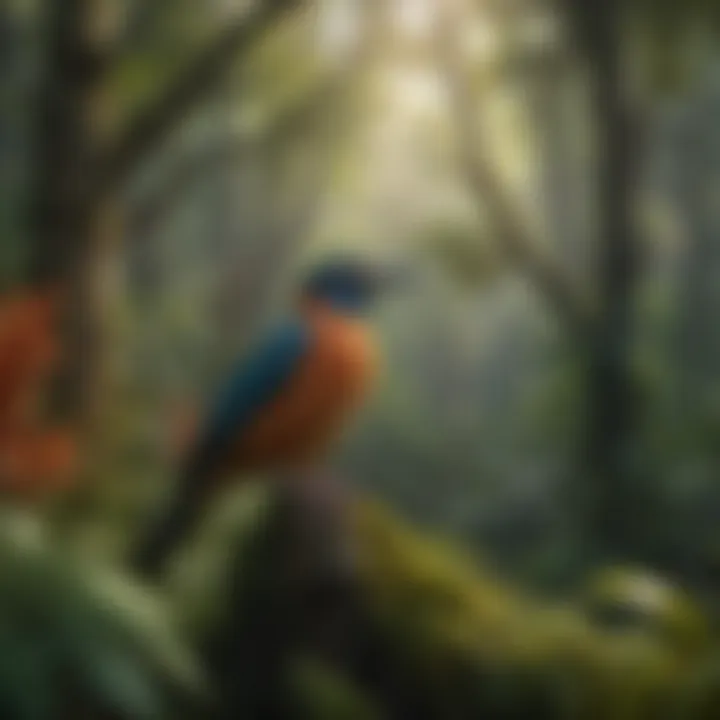
Fauna of the Caribbean National Forest
The fauna of the Caribbean National Forest is equally diverse. Bird species such as the Puerto Rican Spindalis and the endangered Puerto Rican Parrot inhabit the tree canopies, while reptiles like the Puerto Rican Boa are found in the underbrush. Mammals, including the endemic Puerto Rican Hutia, contribute to the ecosystem’s complexity as they interact with their environment.
Insects also play a vital role in pollination and decomposition. The presence of such a variety of animal life indicates a healthy ecosystem, this is essential for ecological balance and the survival of many plants. The unique adaptations of these species to the forest environment are significant for understanding biodiversity dynamics.
Endemic Species and Conservation Status
Endemic species in the Caribbean National Forest draw particular attention due to their unique evolutionary history. These species, which are found nowhere else on Earth, contribute to the forest's uniqueness. However, many endemic species are threatened due to habitat destruction and climate change.
The Puerto Rican Parrot, for instance, has experienced drastic population declines. Efforts to conserve this species have become vital. Conservation initiatives focus on habitat protection and restoration, aiming to create a sustainable environment for these birds.
Additionally, ongoing research aims to monitor and document endemic species to better understand their ecology. This knowledge will aid in developing effective conservation strategies, vital for ensuring the survival of both the species and the rich biodiversity of the Caribbean National Forest.
"Biodiversity is the bedrock of ecosystem resilience, influencing both ecological function and human wellbeing."
The biodiversity of the Caribbean National Forest is crucial not only for maintaining ecological integrity but also for supporting local communities and economies. Understanding the flora and fauna facilitates informed decision-making in conservation policies and practices.
Ecological Significance
The ecological significance of the Caribbean National Forest cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of various ecosystems, supporting both local wildlife and plant life. This forest acts as a vital reservoir of biodiversity, offering habitat and sustenance for numerous species. As urban areas expand, understanding the ecological importance of such regions becomes increasingly critical.
Ecosystem Services Provided
Ecosystem services in the Caribbean National Forest are varied and essential for both the environment and human populations. These services can be categorized into four main types:
- Provisioning Services
The forest provides a range of natural resources, including timber, fruits, and medicinal plants. Local communities rely on these resources for sustenance and economic activities. - Regulating Services
These services include air and water purification, pollination of plants, and pest control. Healthy forest ecosystems help regulate local climates, mitigate floods and droughts, and maintain soil fertility, which benefits agricultural practices. - Cultural Services
The forest holds cultural significance for local communities. It is a site for recreation, education, and spiritual practices. The richness of biodiversity enhances ecotourism, providing economic opportunities for locals and fostering environmental awareness. - Supporting Services
These are fundamental processes such as nutrient cycling and soil formation that enable ecosystems to function effectively. The integrity of these processes is necessary for the long-term sustainability of the forest.
"Ecosystem services are the backbone of natural resource management and conservation in the Caribbean National Forest."
Understanding these services is vital for effective forest management and conservation strategies. Without them, both natural and human communities may suffer.
Role in Climate Regulation
The Caribbean National Forest plays a significant role in climate regulation. Through processes like photosynthesis, the forest sequesters carbon, effectively reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This is crucial in combatting climate change. Forests are known to influence weather patterns, impacting rainfall distribution and temperature moderation.


The forest’s biodiversity also enhances its resilience against climate fluctuations. A diverse ecological community can adapt better to changes, thereby maintaining ecological balance.
In addition, the forest helps buffer local areas from extreme weather events, such as hurricanes. Intact forest ecosystems can significantly lessen the impact of storms by providing protection to coastal areas and reducing erosion.
Understanding and preserving these ecological functions is essential for the long-term health of the Caribbean National Forest and its surrounding environments.
Cultural and Economic Aspects
The interaction between the Caribbean National Forest and local populations plays a significant role in both cultural identity and economic viability. This forest is not merely a patch of land but a vibrant ecosystem that has shaped the customs, livelihoods, and community dynamics of the people inhabiting the surrounding areas. Understanding these cultural and economic aspects is crucial for appreciating the forest's holistic importance.
Local Communities and Their Relation to the Forest
Local communities have a deep-rooted connection with the Caribbean National Forest. Their history is intertwined with this rich environment. Many families have lived for generations near the forest, sourcing food, traditional medicines, and materials from its diverse flora and fauna.
This life cycle creates a symbiotic relationship. These communities act as stewards of the land, engaging in sustainable practices. They often participate in reforestation projects and conservation efforts, understanding that their well-being is tied to the health of the forest. Indigenous knowledge contributes to effective resource management, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity.
In many ways, the forest reflects the cultural heritage of these local people. Festivals and rituals often celebrate the unique flora and fauna, highlighting the intrinsic value of the forest. This creates an opportunity for education about ecological significance and emphasizes respect for nature among younger generations.
Tourism and Its Impact
Tourism is a vital component of the economy surrounding the Caribbean National Forest. Visitors are drawn to its breathtaking landscapes and biodiversity. This influx of tourists generates revenue and job opportunities for the local communities, enhancing their economic well-being.
However, tourism brings both benefits and challenges. On the positive side, a well-managed tourism sector fosters awareness about conservation and promotes the forest’s ecological importance. Eco-tourism initiatives educate visitors about the fragile ecosystems in the forest. It offers tours led by knowledgeable locals, which enhances visitors’ experiences and respects cultural contexts.
On theother hand, if tourism is not managed correctly, it can lead to negative impacts, such as habitat degradation and increased waste. Hence, establishing regulations is essential. Engaging local communities in tourism planning is key to ensuring that the cultural integrity and ecological sustainability of the Caribbean National Forest are maintained.
The Caribbean National Forest serves as a bridge connecting local communities to global ecological discussions, illustrating how local customs can enrich conservation efforts.
Consequently, to balance economic needs with ecological health, it is vital to emphasize sustainable tourism practices. These should be based on principles that conserve the environment while providing meaningful economic benefits to local populations.
Conservation Efforts
The preservation of the Caribbean National Forest is vital for maintaining its unique ecosystems and the biodiversity within. Various conservation efforts have been established to address challenges faced by this crucial environment. These initiatives offer numerous benefits, protecting the forest's integrity and supporting local communities. Conservation is indispensable, as it links ecological health with human well-being.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government intervention plays a significant role in the conservation of the Caribbean National Forest. Policies implemented at the local and national levels foster sustainable practices that mitigate environmental degradation. Legislation focuses on regulating land use, preventing illegal logging, and protecting endangered species.
Key policies include protection laws aimed at preserving wildlife habitats. Regulations are also in place to monitor tourism developments, ensuring minimal environmental impact. For instance, the Endangered Species Act is crucial in safeguarding vulnerable species within the forest.
Furthermore, the establishment of protected areas enhances conservation efforts. It restricts exploitative activities while promoting responsible tourism. These areas act as refuges for numerous plant and animal species that thrive within the ecosystem. Each policy contributes to a larger framework aimed at fostering ecological balance.
Community Involvement and Initiatives
The success of conservation efforts heavily depends on community involvement. Local populations often have the most intimate knowledge of the forest's ecology. Engaging these communities allows conservation initiatives to become more effective and culturally relevant.
Local organizations frequently collaborate with governmental bodies to implement grassroots initiatives. These programs aim to educate residents about sustainable practices, resource management, and habitat preservation. For example, workshops on reforestation efforts empower communities to contribute tangibly to the forest's future.
Community-led monitoring programs, such as citizen science projects, enable locals to record biodiversity data. This data supports scientific research and informs policy decisions.
Local community involvement not only encourages sustainable practices but also fosters a sense of ownership and pride in the natural environment.
Conservation of the Caribbean National Forest necessitates a dual approach involving both strong governance and grassroots initiatives. This integrated strategy ensures that both the ecological health of the forest and the livelihoods of local communities are prioritized.
Challenges Facing the Caribbean National Forest


The Caribbean National Forest faces a multitude of challenges that jeopardize its ecological integrity and the services it provides. These challenges stem primarily from human activities and climate change, affecting both the diverse species that inhabit it and the local communities that depend on its resources. Addressing these issues is essential not only for the sustainability of the forest itself but also for maintaining the delicate balance of the surrounding ecosystems.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
Deforestation is one of the most pressing issues confronting the Caribbean National Forest. This phenomenon occurs primarily due to agricultural expansion, urban development, and infrastructure projects. As land is cleared for farming or construction, habitat loss occurs, which directly impacts the myriad of plant and animal species that depend on these habitats for survival.
- Agricultural practices, particularly those related to sugarcane and coffee farming, often lead to the degradation of soil and water resources.
- Urban encroachment can fragment the habitats, making it difficult for wildlife to thrive and reproduce.
The alteration of land use not only threatens wildlife but also affects local communities. While economic benefits may arise from agricultural and urban development, these short-term gains often come at the cost of long-term ecological stability. Local stakeholders need to find a balance that supports their livelihoods without compromising the forest's health. Sustainable land management practices could mitigate some of these impacts, promoting both economic growth and forest conservation.
Climate Change Implications
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Caribbean National Forest. As temperatures rise and precipitation patterns shift, the ecosystems within the forest face serious repercussions.
- Increased temperatures can cause stress on various species, leading to changes in population dynamics and possibly extinctions.
- Altered rainfall patterns affect the growth of vegetation, changing the structure and function of the forest and its ability to sequester carbon.
Moreover, climate impacts are often compounded by human activities. As sea levels rise, coastal regions may experience increased salinity, pushing both terrestrial and aquatic species out of their natural habitats. This dynamic can lead to a decline in biodiversity, affecting everything from nutrient cycles to predator-prey relationships found within the forest.
"The Caribbean National Forest serves as a critical refuge for many species; understanding the implications of climate change is vital to developing effective conservation strategies."
In summary, the challenges facing the Caribbean National Forest are multifaceted and require immediate attention. Deforestation and climate change are not isolated issues but interconnected challenges that have profound implications. Only through a combination of conservation policies, sustainable practices, and community engagement can we hope to protect this invaluable ecosystem.
Future Directions for Research and Policy
The evolution of research and policy regarding the Caribbean National Forest is crucial for ensuring both its preservation and sustainable use. As environmental challenges become more complex, innovative and forward-thinking approaches are necessary. Scholars, conservationists, and policymakers must continuously adapt to emerging issues, particularly those arising from climate change, habitat loss, and biodiversity concerns. Focusing on unique and effective conservation strategies can lead to better outcomes for this valuable ecosystem.
Innovative Conservation Techniques
Innovative conservation techniques involve the integration of modern science, technology, and traditional practices to enhance biodiversity conservation efforts. These techniques can significantly improve our understanding of the complex interactions within the forest's ecosystem.
Recent studies emphasize:
- Remote Sensing: Utilizing drones and satellite imagery to monitor forest health and track deforestation in real-time.
- Genetic Research: Applying genetic tools to assess species diversity and identify populations at risk. This provides insight into where conservation efforts are most needed.
- Habitat Restoration: Implementing novel approaches for restoring degraded areas, including the use of native plant species that require less management and provide habitat for local wildlife.
Importantly, collaboration among multidisciplinary teams can lead to shared insights and resources, allowing for more comprehensive conservation initiatives.
Education and Outreach Programs
Education and outreach programs play a pivotal role in fostering community engagement and awareness regarding the importance of the Caribbean National Forest. These programs can empower local populations to take active roles in conservation.
Aspects of effective outreach include:
- Workshops and Seminars: Organizing events not only raises awareness but also provides crucial training on sustainable practices.
- Volunteer Programs: Encouraging local residents to participate in forest clean-up days or conservation projects helps to build a sense of ownership among community members.
- Collaboration with Schools: Developing curriculum that includes local ecology and conservation can inspire future generations to value and protect their environment.
Effective communication of research findings to the public enhances transparency and trust in conservation efforts. It also promotes a culture of stewardship and responsibility toward the forest. By investing in education, communities can develop legacies of sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and local economies.
Epilogue
The conclusion of this article holds significant importance in encapsulating the essence of the Caribbean National Forest. It synthesizes the diverse elements discussed throughout the article and reaffirms the critical role this forest plays in ecological and cultural contexts. The comprehensive overview provides readers a clear understanding of why this national treasure deserves attention and protection.
Summary of Key Points
The article outlined several core themes that are essential for grasping the full scope of the Caribbean National Forest:
- Geographical and Historical Context: Understanding the physical and historical backdrop of the forest helps appreciate its ecological significance and the conservation challenges it faces.
- Biodiversity: The forest is a haven for various flora and fauna, including endemic species that contribute to its unique ecological profile. This biodiversity is not only vital for environmental health but also for local economies dependent on these natural resources.
- Ecological Significance: The forest provides vital ecosystem services like carbon sequestration, which is increasingly crucial in the context of climate change.
- Cultural and Economic Ties: Local communities have a deep-rooted relationship with the forest, relying on it for their livelihoods while contributing to its preservation through sustainable practices.
- Conservation Challenges: Issues such as deforestation and climate change threaten the future viability of the forest, necessitating urgent attention and action.
- Research and Policy Directions: Ongoing studies and innovative conservation techniques are needed to protect this vital ecosystem. Education and outreach programs can foster a greater understanding and engagement with conservation efforts.
Call to Action for Conservation
The need for action to protect the Caribbean National Forest is more pressing than ever. This unique ecosystem demands the involvement of various stakeholders, including governments, local communities, and NGOs. Here are some suggestions for effective conservation efforts:
- Support Local Initiatives: Engaging with local organizations that focus on conservation can amplify efforts to maintain the forest's integrity. Donations or volunteer work can have a significant impact.
- Increase Awareness: Educational programs can enlighten both locals and visitors about the ecological importance of the forest, fostering a culture of preservation.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Encouraging policymakers to enforce regulations that protect the forest's biodiversity is crucial. Public advocacy can influence decisions that affect the forest’s future.
- Participate in Research: Engaging in eco-friendly tourism that supports research initiatives helps in better understanding the ecosystem, increasing its protection.













